Introduction
If you have ever printed out a model from your 3D printer and found wispy strands of filament floating between parts, you're confronted with an issue called 3D print stringing, or 3D print ooze, "hairy prints." As one of the most common issues in 3D printing, it is easy to fix once you realize what you're dealing with.

This guide talks about what causes stringing in 3D printing, how to change your 3D printing retraction settings, and what to do when your 3D print is stringy or has stringing between parts.
What Is 3D Print Stringing?
Stringing in 3D printing, also referred to as oozing, takes place when the melted filament oozes out of the nozzle when the print head travels between two locations of a model. The excess filament gets pulled and stretched into thin threads — that resembles cobwebs — linking the printed components.
It is a universal issue with FDM 3D printing, especially with filaments like PLA and PETG. While minor stringing doesn't ruin a print, it does make the finish look messy and typically requires sanding or trimming.
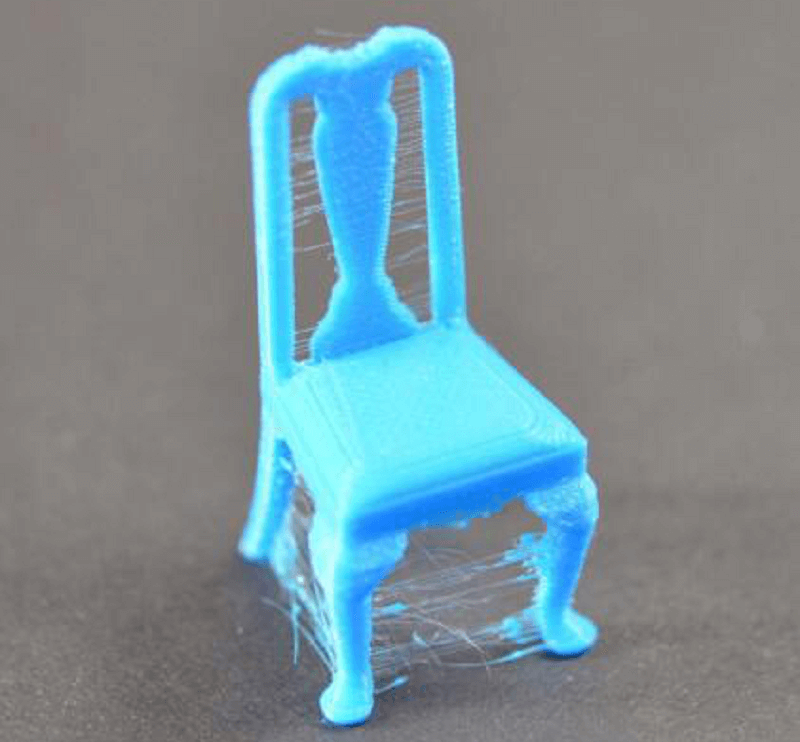
Briefly, oozing is any extraneous leaking of filament, but stringing specifically describes those thin, hair-like filaments deposited behind.
Q: What's the differences between thick and thin stringing in 3D prints?
A: Thin stringing looks like fine hair and is usually caused by mild oozing, slightly high temperature, or low retraction. Thick stringing forms larger blobs and often results from high temperature, disabled retraction, wet filament, or slow travel moves.
A: Thin stringing looks like fine hair and is usually caused by mild oozing, slightly high temperature, or low retraction. Thick stringing forms larger blobs and often results from high temperature, disabled retraction, wet filament, or slow travel moves.
What Causes Stringing in 3D Printing?
The culprit is most often that filaments ooze from the nozzle during travel moves—when the printhead is moving without printing. There isn't one fix for why your 3D print is stringy. Usually, it's a combination of heat, retraction, and filament quality. Let's dive into what can lead to this:
Retraction Settings Are Off or Insufficient
Improper 3D printing retraction parameters are the number one reason for stringing. Retraction controls the retraction distance of filament to be removed into the nozzle prior to moving the head.
Either too low retraction distance or too slow retraction speed will cause not retreating molten filament into the nozzle but dripping during moves.
Printing Temperature Too High
When the nozzle temperature is excessively high, the filament is over-melted and easily extrudes, leading to leaks. This is likely to cause 3D printer thick stringing, especially for filaments like PETG and TPU.
Filament Moisture
Hygroscopic filaments like PETG that tend to soak up water will pop or sizzle when it prints. The water turns into steam and forms bubbles that expel molten filament uncontrollably — resulting in stringy 3D prints.
Slow or Long Travel Moves
As the print head moves slowly or covers long distances, there is a greater opportunity for melted filament to ooze out. Greater travel speeds reduce this effect.
Clogged or Dirty Nozzle
A dirty or partially clogged nozzle will affect pressure inside the hotend, leading to unstable extrusion and excessive oozing in movement.
Hardware issues in some cases, like a worn-out nozzle or bad calibration, will exacerbate the problem.
How to Fix and Prevent 3D Print Oozing
If your 3D prints are beset with fine hairs or blobs of sticky goo, don't panic. Nine times out of ten, it simply comes down to adjusting a few critical settings and getting your filament right.
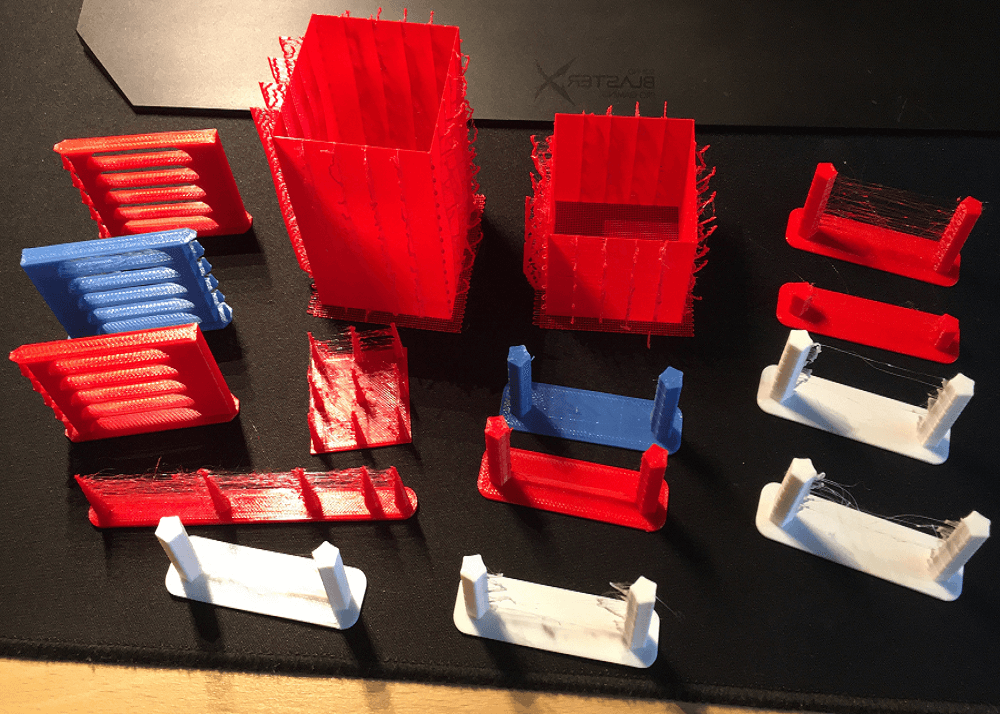
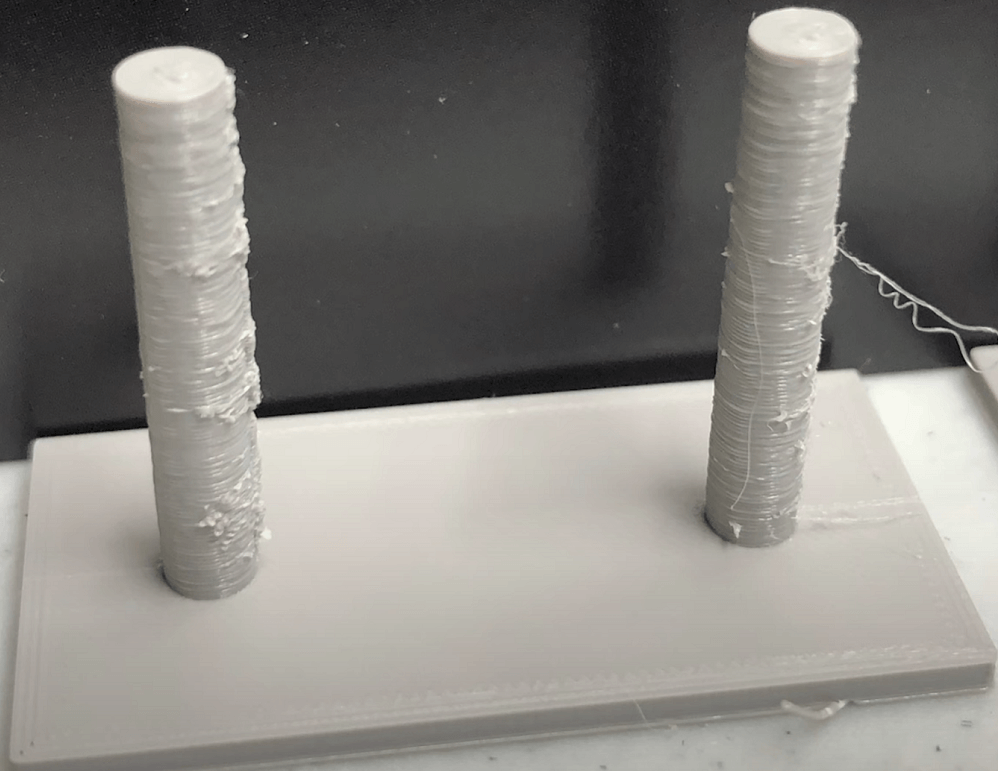
Run a 3D Printing Stringy Test Beforehand
Before you make adjustments to your printers, a 3D printing stringing test can help you see exactly how much oozing your printer is producing. These test models usually have several small towers spaced apart. When the nozzle moves between them, leaked filament strings become visible.
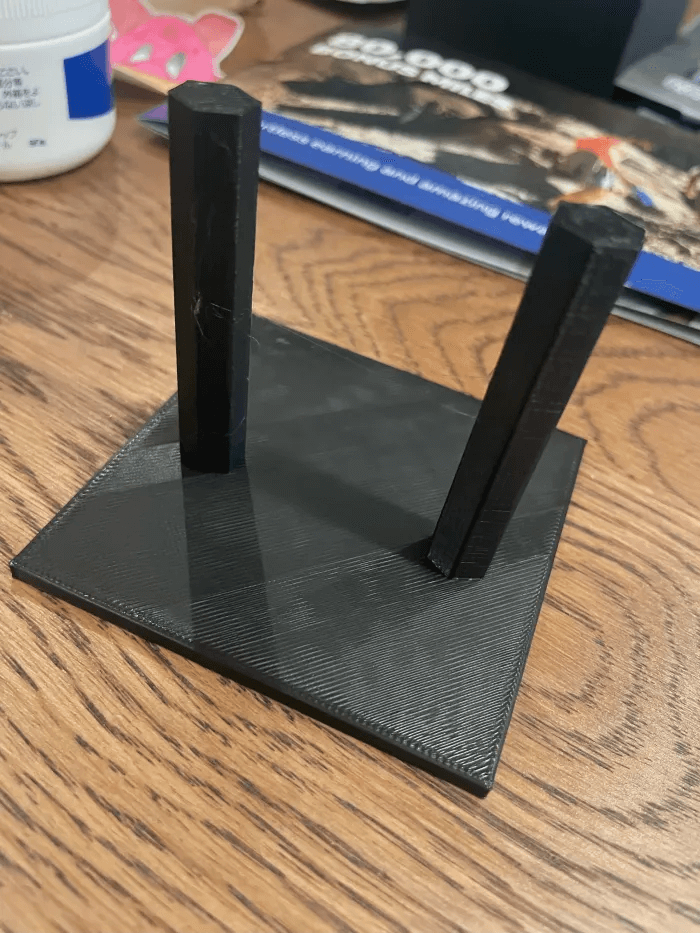

By observing the results, you can identify whether your retraction, temperature, or travel speed needs adjustment. After making changes, re-running the test confirms whether your settings are effective, saving time and material before printing larger parts.
Adjust Retraction and Temperature
Your retraction settings and nozzle temperature are the two most important factors responsible for stringing.

- Enable retraction: Make sure it’s turned on in your slicer.
- Retraction distance: Try 1–2 mm for direct-drive and 4–6 mm for Bowden setups.
- Retraction speed: Start around 25–45 mm/s — fast enough to pull back the filament without grinding it.

- Lower the temperature: If your prints look stringy, lower the nozzle temperature by 5°C at a time until the stringing improves. Avoid going too low, or you may get under-extrusion.
These small adjustments usually remove most of the thin “spiderweb” strands in your print.
Dry and Store Filaments Properly
Moisture-laden filament is also a common cause of 3D print oozing. Warmed wet filament creates steam in the nozzle, which causes molten plastic to be expelled unchecked.
-
Dry the filament: Dry it with a multi-filament dryer box or bake it for 4–6 hours at 50°C (122°F) in an oven.
-
Store it correctly: Keep filament in airtight containers with silica gel packs to prevent moisture absorption.
This is especially important for PLA, PETG, and nylon, which absorb humidity quickly.
You May Also Like: How to Store PLA Filaments
Optimize Travel and Slicer Settings
Your slicer has powerful tools to reduce oozing during non-print moves.
-
Increase travel speed: 150–200 mm/s helps minimize the time the nozzle spends on open air.
-
Combing Mode: Keeps the nozzle moving within printed areas to avoid crossing gaps.
-
Avoid Crossing Perimeters: Reduces unnecessary movement that can cause strings.
-
Wipe or Coast settings: Relieve pressure in the nozzle at the end of each extrusion to stop extra filament from leaking out.
Tuning these features together can make a noticeable difference in the surface quality of your prints.
Material-Specific Tips
Each filament type behaves a little differently, so it’s worth fine-tuning your setup for each one:
-
PLA: Sensitive to temperature and moisture — print around 190–210°C.
-
PETG: Naturally stickier, so try slightly lower temps and longer retraction distances.
-
TPU: Flexible and soft — use minimal retraction or it may clog the nozzle.
-
ABS: Less prone to stringing, but excessive heat can still cause light oozing.
A quick retraction test model is the best way to dial in the right balance before larger prints.
Daily Maintenance and Long-Term Prevention
Finally, good maintenance habits go a long way in preventing 3D printer stringing over time.
-
Upgrade Hardware: Consider a direct drive extruder for better control or an all-metal hotend for high-temp filaments.
-
Clean the Nozzle or Hotend: Regularly clear debris with a brass brush or cold pull to check for leaks and ensure smooth flow.
-
Use Quality Filament: Cheaper brands may have inconsistencies that promote oozing.
With a well-calibrated printer and dry filament, stringing should become a rare issue — not a regular frustration.
FAQs About 3D Printer Stringing
Q: Is thick stringing different from regular stringing?
A: Yes, most of the time it's due to over-extrusion or hardware issues and creates fatter defects rather than strands.
Q: How do I remove stringing from 3D prints? A: You can remove stringing manually using tweezers, pliers, or scissors to pull off thin strands. A low-heat gun or soldering iron tip can carefully melt small strings. Use fine-grit paper to smooth 3D print surfaces afterward. For ABS, acetone vapor smoothing can also help. Prevention during printing is the best long-term solution.
Conclusion
Stringing may look messy, but it’s one of the simplest 3D printing issues to fix. The key is understanding why stringing occurs in 3D printing — probably too much heat, poor retraction, or damp filament — and then compensating for it. With the proper settings, you'll discover your prints to be cleaner, smoother, and more professional.