People have used extrusion in 3D printing for a long time. It was developed in the 1980s. The term extrusion means that the 3D printer pushes plastic filament through a heated nozzle. This process builds objects layer by layer.
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) use 3D printer extrusion. The extruder in these machines helps ensure that the system feeds and controls the filament precisely.
Our guide below will cover everything you need to know about extrusion in 3D printing. From how it works to the pros and cons and some common issues, so you can be an expert at using your new 3D printer.
What Is Extrusion In 3D Printing?
Extrusion is the process of heating and pushing material. This material is plastic filament. It includes thermoplastics like PLA, ABS, and PETG.
The printer pushes the filament through the nozzle to create 3D shapes layer by layer. The object builds as each layer hardens.
The process is like a hot glue gun on a robotic arm. It heats, moves, and places the material accurately. Extrusion is how FDM 3D printing machines work, controlling the melted filament to create each design.
The process works in both mechanical and thermal systems. The extruder uses gears to grip and feed the filament.
It pushes the filament through the hotend. The hotend heats the filament until it melts. This allows the melted filament to flow through the nozzle.
The print head on the 3D printer moves side to side and back and forth to shape the object. The build plate moves up and down to create each layer and add height.
Components Of a 3D Printer Extrusion System
Each part of a 3D printer ensures that the material places itself correctly when creating a 3D object. The three main parts are the extruder, the hotend, and the filament.
Extruder
This is part of a 3D printer that feeds the filament into the hotend. It has a motor that drives the movement and gears to grip and drive the filament forward. There is also a heat break to keep the cool side and hot side separate.
The extruder consistently moves the filament to the hotend for melting by applying the right pressure.
Extruders can be direct drive or Bowden types. Direct drive extruders are mounted directly on the drive head. Placing Bowden extruders away from the head can help increase printing speed.
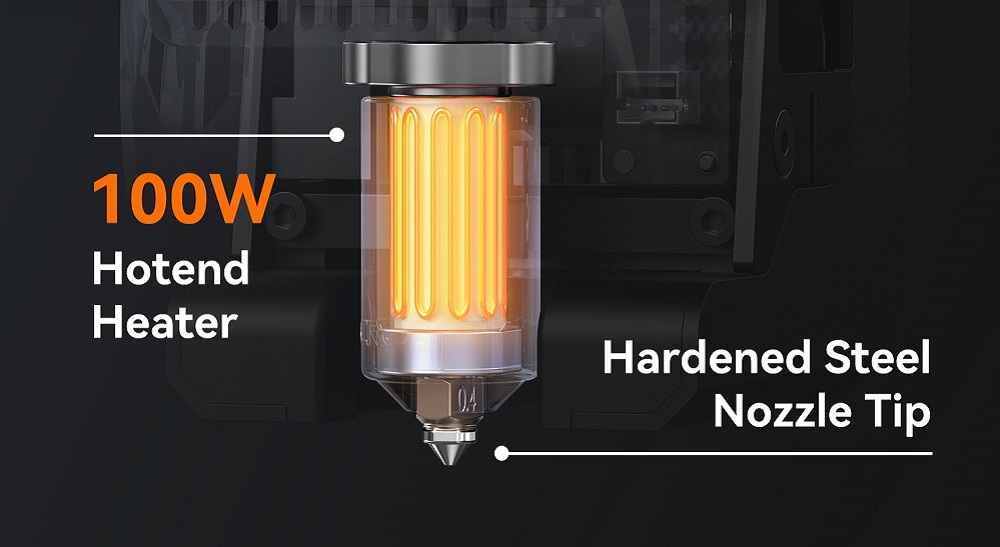
Hotend
So the filament can flow through the nozzle, and it is heated to a melting point at the hot end. It consists of a heating block and a thermistor to keep a consistent temperature for smooth extrusion. Having a high-quality hotend is essential for high-quality finishes and faster print speeds. Clogging of the nozzle and temperature fluctuations can be issues if using a poor-quality hotend.
You’ll often find specialized hotends for different filament types.
Filament
This is the printing material made from thermoplastics, which melts when heated and hardens when cooled to make a 3D shape.
Some common types 3d printer filament:
- PLA (Polylactic Acid): This is the easiest filament to print and is eco-friendly.
- ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene): The most heat-resistant and durable.
- PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol): Best balance of strength and printability.
Choosing the right filament is important since using the wrong one could lead to warping. For example, leaving PLA in the heat can cause it to soften if left outside in the sun.
Other parts of a 3D printer (not the extrusion system) include the motherboard, power supply unit, frame, interface, USB/SD card slot, print bed, and cooling fans.
How Does An Extrusion 3D Printer Work?
We’ve broken down exactly how the extrusion process works below.
- Step one: A machine winds the filament onto a spool. The extruder pulls the filament from the spool to feed it into the hotend.
- Step two: Heat the filament inside the hotend until it softens. Different types of filament will melt at different temperatures. ABS, for example, melts around 230-270 degrees while PLA melts at 190-230 degrees. Temperature control is important as too cold can cause jams and too hot can lead to deformed prints.
- Step three: Push the filament through the fine nozzle to control the thickness of the material.
- Step four: The melted filament builds layer by layer to create a 3D object. The print head moves along the X, Y, and Z axes to form the shape. X and Y are for horizontal movements, while Z controls the layer height.
Our 3D printers at Creality have thermistors and advanced parts. They automatically keep the right temperatures for your filament.
Types Of Extrusion In 3D Printing
As we briefly mentioned earlier, there are two main types of extrusion methods in 3D printing, known as Direct Drive and Bowden.
Direct Drive Extruders
Direct drive extruders have the extruder motor mounted directly on the print head above the hotend. The filament has a small distance to travel before it softens and gets extruded.

Pros
- Great for flexible filament since there is less room for the filament to bend during feeding, which is great for flexible filament like TPU.
- Quick retraction gives more precision and reduces stringing. Our Creality Hi Combo uses a direct drive extruder for more reliable printing.
Cons
- Added weight on the print head can slow printing speed.
Bowden Extruders
Bowden extruders have the extruder motor located away from the printhead and mounted to the printer's frame. The filament is then pushed through a long Teflon tube to get to the hotend.
Pros
- A lighter printer head means a faster print speed.
- Ideal for larger format prints since it has reduced weight.
Cons
- Not suitable for flexible filaments due to the long tube.
Benefits Of Extrusion 3D Printer
Extrusion 3d printers are one of the most commonly used types of printers due to the following reasons:
- Cost-effective: These types of 3D printers are more affordable in comparison to resin ones and work with a larger variety of filaments. An extrusion 3D printer is perfect for beginners and professionals.
- High precision: They can produce smooth surface finishes and sharp shapes with accurate layer-by-layer construction.
- Easy to use: You need minimal training to use a 3D extrusion printer, with most now having easy-to-use interfaces.
Jetting Vs Extrusion - What's The Difference?
If you're comparing 3D printing technologies, extrusion 3D printing is the better option for beginners, and jetting is better for making high-detail aesthetic models; they also tend to come at a higher price.
The jetting process works by dropping tiny drops of material onto the build surface, which hardens to create the shape.
Common Problems & How To Fix Them
Clogged Nozzle
Uneven prints and print failure can occur from a clogged nozzle. To fix this, you can use a cleaning needle to clear stuck material or do a cold pull by heating the nozzle and then manually pulling out the filament.
To prevent this, always perform maintenance and avoid leaving the nozzle hot when you aren’t printing to stop the filament from burning.
Under-Extrusion
Not enough filament comes out of the nozzle, which can cause gaps and missing parts in your prints. To fix this, make sure the filament spool isn’t stuck, increase the temperature, increase extrusion in your slicer settings, and inspect for any blockages.
Over-Extrusion
Too much material is coming out, causing messy details and blobs. To fix this, reduce the extrusion flow rate in your slicer settings, lower the nozzle temperature slightly, or check the filament diameter settings.
Applications Of Extrusion In 3D Printing
- Prototyping - Designers can quickly turn their digital models into physical prototypes, saving time.
- Custom parts - These could include dental models or automotive parts like brackets. They can be made with exact dimensions and are an ideal alternative for traditional manufacturing, thanks to their fast speed.
- Art & Design - Whether it’s designed like jewellery or custom sculptures, artists can use these machines to bring their ideas to life using colourful filaments if needed.
The Future Of 3D Printer Extrusion With Creality
Whether you're an engineer or a beginner, extrusion is one of the easiest 3D printing methods out there for producing prototypes of functional parts. Our 3D extrusion printers at Creality can help build your creative projects with powerful and precise tools such as our creality hi combo, which is under $600 and perfect for beginners.
The future of 3D extrusion printing is only going to get better with higher temperature hotends, the introduction of multi-material printing, and industrial-grade filaments for designing more durable parts for aerospace and other industries.
