While 3D printing progresses, Multi Jet Fusion (MJF), an additive manufacturing technology crops up as an exceptional innovation, leading the industry. Nowadays, engineers and creators have multiple opportunities regarding numerous 3D printing technologies and materials at hand.
Multi Jet Fusion 3D printing is an innovative process that reshapes the way products are outlined and made; it’s modifying whole industries by providing unparalleled accuracy, adaptability, and efficiency. Join in as we delve into the landscape of MJF 3D printing, analyzing how it works, its advantages, and its evolutionary capability across several sectors.
What is MJF 3D Printing?
What is MJF 3D Printing? Multi Jet Fusion is among the latest additive manufacturing technologies available and has vast potential.
Developed by HP in May 2016, Multi Jet Fusion is an advanced MJF 3D printing process, particularly tailored for industrial production.
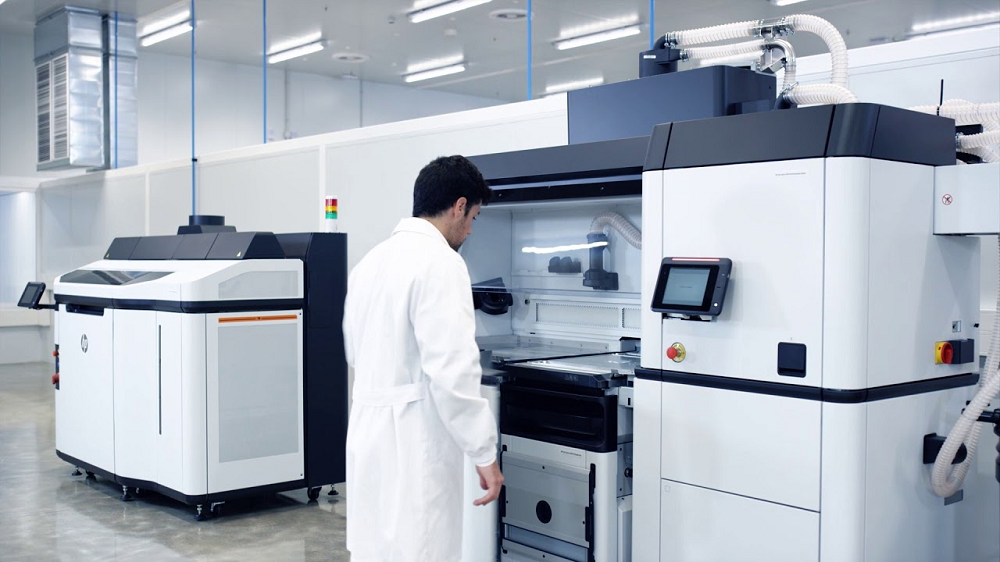

Besides, MJF is a part of the powder bed fusion family, a kind of Binder Jetting 3D printing technology.
Far from classic printing processes, MJF utilizes a unique technique by implementing the two blending and describing agents over a bed of powdered matter _ usually TPU or nylon that is then mixed by heating components to make complex layers.
This method guarantees great precision and creates components with superior mechanical characteristics and minute detail.
Also, HP declares that MJF 3D printing is cost-effective and speedy, and manufactures more useable parts than opponent technologies. Strangely enough, over 140 MJF printed parts are active in every MJF 3D printer.
The Power of MJF to tackle complicated geometries and make very long-lasting things confirms it as a popular choice among businesses considering going beyond the limits of classic manufacturing.
While MJF technology isn't currently in our product lineup, the Creality K2 Plus represents the cutting edge of FDM 3D printing innovation. Click to see why professionals are choosing this advanced manufacturing solution.

How Does MJF 3D Printing Work?
The MJF 3D printing process is complicated and captivating, It includes numerous crucial steps to transform powdered medium into strong three-dimensional items.
That said, an MJF 3D printer consists of nearly a print bed, material recoated, and thermal inkjet array. Multi Jet Fusion 3D printing operates in this way:
-
Step 1: Powder Applying - First, a light coat of powder material is spread evenly over the print bed by recoated material. Then, the ink heads of printers begin printing the initial layer.
-
Step 2: Agent Application - The print heads pass over the print bed, and fusing and detailing agents are applied onto the powder bed in areas corresponding to the part's geometry following the digital design directions. That said, the detailing agent manages the grain and completes the end product. However, the fusing agent assists in describing the parts to be hardened.
-
Step 3: Fusing Procedure - The detailing and fusing agents are temperature-sensitive, so this is how the wonders unfold. The region is exposed to infrared heat that stimulates the fusing agent, bringing the powder particles to connect and create a hard layer.
-
Step 4: Layering - The build plates go a little lower, and the material recoater distributes a new layer of powder. The procedure repeats, forming the item layer by layer.
-
Step 5: Cooling and Extraction - When the MJF 3D printing process finishes, the build unit is shifted to a cooling stop where it slowly chills to harden the components wholly. Following cooling, the extra powder is taken out, which is mostly recyclable. Also, the components go through more post-processing like surface finishing and coloring.
MJF vs Selective Laser Sintering vs FDM 3D Printing: Key Differences
Although MJF is much the same as Selective Laser Sintering (SLS), various significant differences appear between the three technologies, each influencing the selection of technology depending on the particular specifications of a task. Here’s everything about MJF vs. SLS 3d printing.
In comparison, injection molding offers less flexibility and longer lead times but can be more cost-effective for large production runs due to lower per-unit costs once the mold is created.
Material
Mainly, MJF utilizes TPU and nylon, substances famous for their adaptability and longevity. This makes them perfect for manufacturing 3D printed working parts that demand strength and accuracy.
Also, SLS employs nylon but expands to further polymers. However, FDG provides an extensive variety, involving ABS, PLA, and PETG, which are known for their user-friendliness in less intricate uses.
Layer Fusion
The MJF 3D printing process involves jet fusion work, where a fusing agent is applied using an inkjet array along with infrared heat to attach powder drops. This technique notably improves the toughness and precision of the components.
On the contrary, SLS utilizes laser sintering, which MJF does not use. This process is slow and mostly causes uneven surface finishes. That said, FDM dissolves and extrudes thermoplastic filament coat by coat, which is evident in the end product and might impact its durability.
Surface Finish
Among MJF's striking characteristics of MJF is its power to attain a polished and even surface finish. This finish is greater than the coarse finishes standard of SLS and the layered texture of FDM prints.
So, MJF is more appropriate for creating off-the-rack elements without immense post-processing.
Speed and Efficiency
Typically, MJF is speedier than SLS because it applies to fuse and detail agents simultaneously over the whole layer instead of the exhaustive sintering procedure utilized in SLS.
In contrast to FDM, MJF is quicker and more qualified to make parts with minute details and natural attributes.
Post-Processing
Although every single technology needs some post-processing, MJF generally demands minimum because of its neat finish. Also, due to the lack of supporting frames, mostly required in FDM. a processing station plays a crucial role in cooling the printed parts and facilitating the removal of excess powder.
MJF is best for manufacturing sturdy, high-detail operating components as it uses accurate inkjet arrays to implement heat and fusing agents, confirming layers connect ideally without bending.
Advantages of MJF 3D Printing
If you want to make working prototypes and comparatively small end-use parts, then MJF is your quick fix. This makes it perfect for functional prototyping and end-use parts, emphasizing the importance of accuracy and mechanical strength. Here’s the detail:
Precision and Accuracy
Multi Jet Fusion 3D printing attracts attention because of its amazing clarity and accuracy. This makes it perfect for effective prototypes and end-use parts. The innovation can also tackle complicated details and intricate geometries that are difficult for other 3D printing methods. Therefore, it’s the favored choice for businesses that need great precision for real designs.
Speed
Because of the competent layering procedure of technology, MJF can create components quicker than classic SLS printing. This pace makes MJF specifically beneficial in a commercial environment where time is crucial. This empowers industries to boost product-making cycles and lead goods to market faster.
Mechanical Properties
MJF 3D printing is superb for manufacturing very far more powerful components compared to SLS production. Components made with MJF are recognized for their strong mechanical characteristics with rupture strength of utmost XY and Z 48 MPa/6,960 psi and longevity.
This ability allows the innovation to be operated in making operating elements that can resist functional pressure like mechanical parts and complicated construction. The multi jet fusion work process involves an inkjet array for the selective application of fusing and detailing agents on a bed of nylon powder, constructing each layer by depositing powder and fusing it together until the part is fully built.
Smooth Surface Finish
MJF provides a leveled surface finish than several further printing technologies, lowering the requirement for extra post-processing. That said, quality is necessary when making parts that need great artistic value or when more surface treatments are considered. For instance, sealing or painting.
Support-Free Structures
Contrasted to FDM which mostly needs support frames that should be eliminated post printing, MJF employs not sintered powder to assist intricate features and projections in the printing procedure. This property restores time and lowers material left over.
Limitations of MJF 3D Printing
Like any other technology, Multi Jet Fusion 3D printing comes with its limitations. Here’s the detail:
-
Equipment Cost: The most considerable blockade to the worldwide support of MJF technology is the great price of the tool. Typically, MJF printers are commercial equipment that needs a large investment. That said, it can be unaffordable for small industries or individual consumers.
-
Material Limitations: Although MJF brings exceptional outcomes with substances such as TPU and nylon, its scope is relatively finite than other 3D printing technologies.
-
Post-Processing Requirements: Regardless of the finest finishes attainable with MJF, a bit of post-processing is always needed. This could involve powder disposal, and possible dyeing or painting to reach the preferred artistic characteristics.
Applications of MJF 3D Printing
MJF 3D printing is typically beneficial in contexts demanding average temperature resistance and strength. Here are particular applications of MJF 3D printer:
-
Automotive: The automotive business uses Multi Jet Fusion 3D printing to create long-lasting and lightweight components that resist the hardships of routine use. Parts like housings, brackets, and intricate ducts are made with accuracy.
-
Medical: Of course, the medical field profits notably from MJF technology, specifically in the making of specialized prosthetic limbs and orthotic tools. The objects are made to suit specific patients ideally, offering better usefulness and ease.
-
Consumer Electronics: Regarding consumer electronics, MJF is best for manufacturing strong casings, complex button assemblage, and further parts that need accurate dimensional balance.
-
Industrial Prototyping: MJF 3D printing is widely employed for working prototyping in several businesses, empowering industries to check and modify their outlines without the great charges and prolonged delays linked with classic production processes.
-
Customized Manufacturing: One more area where MJF attracts attention is bespoke production. It allows cheap production of custom-made items without the requirement for setting expenses or costly molds.
How to Get Started with MJF 3D Printing?
To begin with MJF 3D printing, first choose an MJF 3D printer. This includes the particular requirements of your jobs, like material needs, print sizes, and the predicted print volume.
It is also important to be aware of the design restrictions linked with MJF technology. Moreover, the paper explores numerous post-processing techniques needed to complete MJF prints, like surface smoothing, powder disposal, and coloring.
That said, efficient upkeep of MJF 3D printers is crucial for confirming their durability and production.
Conclusion
In short, what is MJF 3D printing? MJF 3D printing speaks for considerable progress in the domain of additive manufacturing, providing a mixture of accuracy, pace, and adaptability that is unsurpassed by older technologies. Even if you’re seeking to modernize automotive design, overcome the limitations of the medical field, or just study the promise of innovative 3D printing, MJF offers the equipment essential to understand working, complicated, and customized items.
