
As higher education institutions strive to bridge theory and practice in STEM education, access to reliable prototyping technologies has become a decisive factor. At Germany's Hamburg University of Technology, Creality’s advanced 3D printing solutions have enabled a new generation of engineering education—ideas are rapidly transformed into functional prototypes, and students engage deeply with real-world engineering challenges. At the Institute for Smart Engineering and Machine Elements (ISEM), led by Professor Nikola Bursac, 3D printing is not treated as a tool, but as a key element of teaching, research, and innovation.
Challenges in Engineering Design Before Advanced 3D Printing
A key part of the institute's research and teaching is to make the development process tangible for students by creating spaces where ideas quickly become concrete, and prototypes serve as a foundation for learning, discussion, and innovation. Prototyping is not just a technical process but a essencial factor for both educational approach and research activities.
However, the institute used to face significant limitations. The existing entry-level machines lacked precision, reliability, and material diversity for complex engineering designs and applications. Printing processes were often error-prone, leading to high failure rates and unnecessary task delays.
As a result, in lectures, students could only access simple demonstrations while they were expected to test concepts quickly or get deeply involved in more challenging projects. In research, projects could only be realized to a limited extent that required rapid iterations and close integrations of digital models and physical prototypes. The institute hence needed a more powerful, reliable and scalable solution to fully unlock the potential of modern STEM engineering design.
Creality-Powered Projects: From a Billiard Robot to the GSD Module
The introduction of Creality’s 3D printers—including K1C, K2 Plus, and CFS systems—marked a turning point. Deployed as robust powerhouses, the printers were strategically integrated into the core teaching and research workflows.
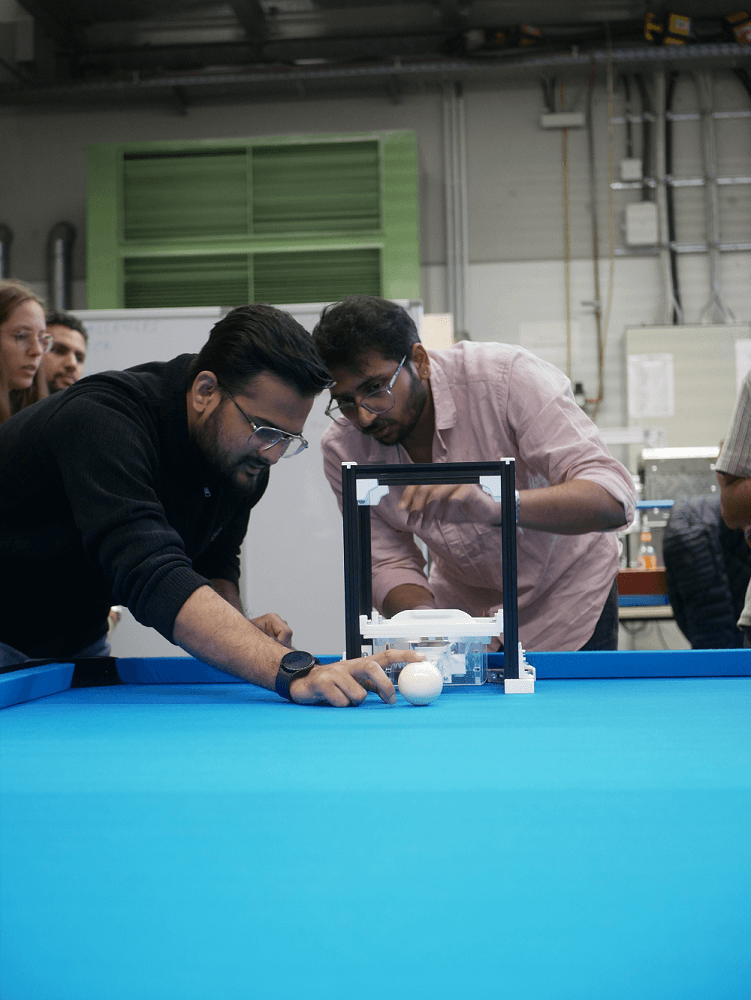
One impactful example is the Mechanical Design Project, which represents a cornerstone of the Bachelor’s program. Here, students work in teams throughout the semester on the development of a complex mechatronic system. Specifically, they design a billiard-playing robot, whose key component is a mechanical striking unit. The unit must be designed and manufactured to function precisely, reproducibly, and robustly. With Creality printers, key components, housings, and interfaces can be produced in short iterations, allowing students to directly test physical prototypes and accordingly refine designs.
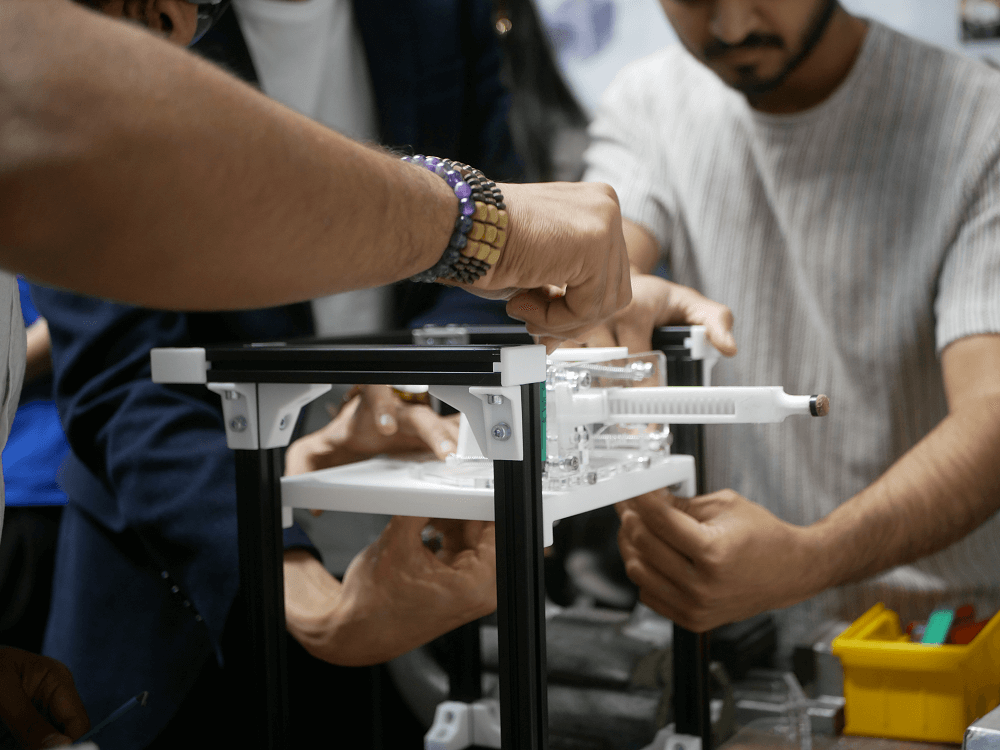
As Professor Bursac observes, “The printing systems have raised the speed, quality, and diversity of our projects to a new level. They allow us to view prototyping no longer as a limiting factor but as a true driver of innovation in both teaching and research.”
Another notable application is the Generational Sheet-Metal Development (GSD) module, where student teams design a new generation of grills each year. Creality’s 3D printers are applied to manufacture functional prototypes, fixtures, and testing adapters, significantly improving efficiency and design quality. The continuous workflow—from digital designs, building to experiments—makes the development process becomes more tangible, engaging, and educational.
Create Value for Learning Outcomes and Research Advancement
The impacts of Creality’s 3D printing solutions have been profound. Prototyping cycles that once took weeks are now completed in days or even hours. This acceleration enables a steeper learning curve for students. They now gain hands-on experience more quickly and frequently, thus identifying design flaws and understanding the real-world consequences of engineering decisions. This leads to higher motivation, stronger problem-solving skills, and a clearer connection between STEM theory and application.
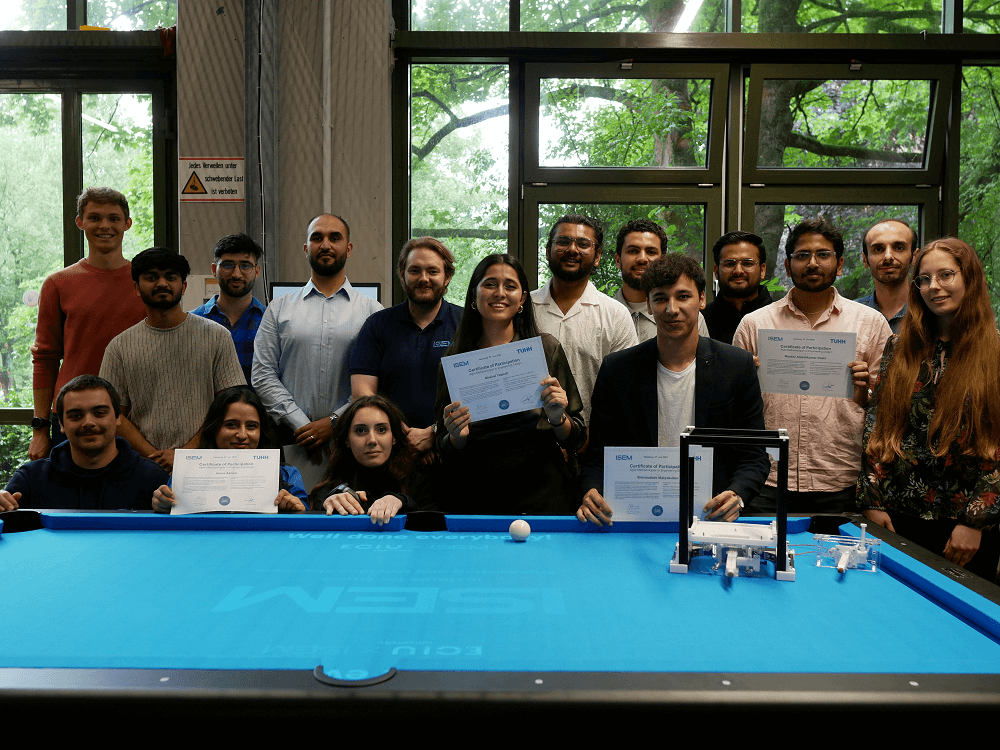

In research, concepts that were previously discussed only at a theoretical level can now be physically tested and validated. Researchers can rapidly build test rigs, compare design variants, and make data-driven decisions, enhancing solid research outcomes and facilitating their transformation within the industry.
Forging a Future of STEM Innovation
Creality’s collaboration with ISEM is more than a technology partnership—it’s a commitment to advancing STEM education and academic research. By providing reliable, high-performance 3D printing solutions, Creality has bridged the gap between theory and practice, empowering students and researchers to unlock their full potential.
Looking ahead, ISEM plans to expand the use of Creality’s technology into new STEM frontiers, including research on Design for Additive Manufacturing and outreach programs to inspire young technical talents. As Bursac envisions, a long-term partnership with Creality will further drive innovative teaching and research.
